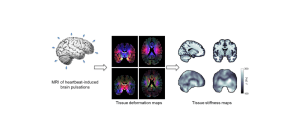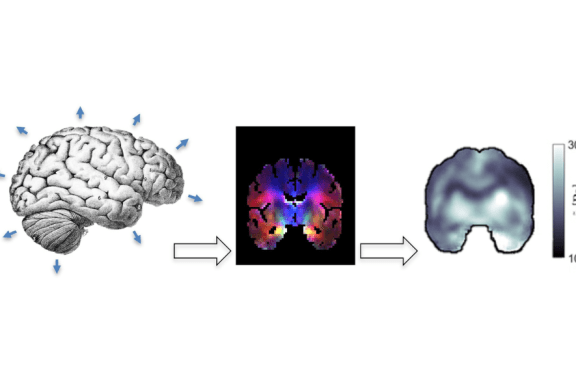
Seismology of the brain refers to quantitative MRI measurements of the subtle brain tissue pulsations that are induced by the heartbeat. These measurements are processed into detailed 3D brain tissue deformation maps that describe the full strain tensor of the deformation over the cardiac cycle. These maps have whole brain coverage with typical spatial resolution of 3 mm isotropic, and a temporal resolution in the order of 50 to 100 ms.
Various parameters can be derived from these strain maps that carry information of the tissue microstructure (such as the brain tissue stiffness) and the embedded (micro)vasculature, such as the volumetric strain of the tissue which reflects the amount of vascular swelling during the systolic phase of the cardiac cycle.
The method is available for both the MRI clinical and preclinical 7T MRI scanners.